[ad_1]
The eurozone’s financial downturn is about to be milder than anticipated, with a carefully watched ballot of the area’s corporations signalling that pressures weren’t as unhealthy as analysts had feared.
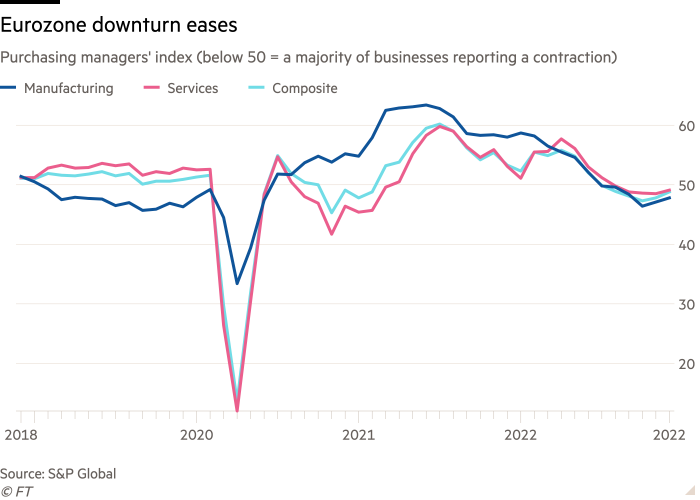
S&P International’s flash eurozone composite buying managers’ index, a gauge of enterprise situations, rose to 48.8 in December — the very best degree in 4 months and up from 47.8 in November.
The studying was additionally above the 48 determine forecast by economists polled by Reuters.
Whereas a rating beneath 50 alerts nearly all of the hundreds of buying managers polled nonetheless suppose situations worsened over the previous month, the tempo of contraction in exercise will not be as nice because it was in the course of the earlier month.
Chris Williamson, chief enterprise economist at S&P International Market Intelligence, stated that “whereas the additional fall in enterprise exercise in December alerts a powerful risk of recession, the survey additionally hints that any downturn shall be milder than thought doubtless a couple of months in the past”.
The survey’s forward-looking indicators, which monitor new orders that companies obtain, “are at the moment boding nicely for the speed of decline to ease additional within the first quarter”.
The overwhelming majority of analysts anticipate the eurozone economic system to contract within the fourth quarter on account of surging vitality costs. Nevertheless, many are actually forecasting a milder recession after fuel costs fell from the report highs seen in the course of the summer season and governments introduced assist packages to defend households and companies from the impression of the upper costs.
“While the eurozone is more likely to undergo a fall in GDP, the PMIs not less than are solely pointing to a modest decline,” stated Ryan Djajasaputra, economist at Investec.
On Thursday, Christine Lagarde, president of the European Central Financial institution, stated she additionally anticipated “a shallow and shortlived recession”. Because of the lively and sturdy labour market, and an easing of provide chain disruptions, she anticipates “that the restoration will decide up” after the recession, leading to 0.5 per cent progress throughout 2023.
The resilience of the economic system and continued excessive inflationary strain prompted the ECB to lift its coverage charge by half a proportion level to 2 per cent on Thursday, and signalling extra half-point rises have been to return.
The survey, based mostly on information collected between December 5 and 14, confirmed that companies’ prices rose on the slowest charge for greater than one-and-a-half years, reflecting the mixture of weakened demand and improved provide.
For the doves on the ECB’s governing council, the cooling in inflationary pressures within the PMIs “will doubtless gas concern that the ECB may find yourself doing an excessive amount of”, stated Bert Colijn, economist at ING Financial institution.
Factories reported the primary enchancment in provider supply instances since January 2020, earlier than the pandemic.
The manufacturing downturn has moderated particularly markedly in December, led by enhancements in exercise in Germany and linked to a mix of higher provide situations and lowered fears of vitality constraints.
The French figures have been the primary disappointment, with its composite PMI dropping once more to a 22-month low of 48, pushed by weak tendencies in providers.
Throughout the eurozone, the service sector malaise has additionally calmed, partially pushed by indicators of a much less intense value of dwelling squeeze and, within the monetary providers sector, fewer issues over the tightening of economic situations.
[ad_2]
Source link


























