[ad_1]
In a nutshell: Interfacing brains with computer systems is difficult. It requires decoding complicated neural indicators, guaranteeing biocompatibility, and stopping immune responses, to call a couple of hurdles. Seamless communication between natural and inorganic techniques requires superior algorithms and exact neural mapping. Latest analysis exhibits that lab-grown “organoids” may assist overcome a few of these obstacles.
Chinese language researchers from Tianjin College and the Southern College of Science and Know-how have created a groundbreaking robotic powered by a tiny organoid derived from human stem cells grafted to a neural interface. This breakthrough system permits the robotic to be taught duties like impediment avoidance and object manipulation.
Described because the “world’s first open-source brain-on-chip clever complicated data interplay system,” the expertise marks a big development in brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) – units that translate between neural and computational indicators.
The South China Morning Publish notes that the scientists grew the organoids from human pluripotent stem cells, which might become numerous cell sorts, together with neural tissue. These synthetic-organic (pardon the oxymoron) mind cells are linked to the robotic’s neural interface, enabling communication between the neural tissue and the robotic’s techniques. Though the offered photographs of pink mind matter are merely mockups (beneath), the precise organoids are a lot smaller.
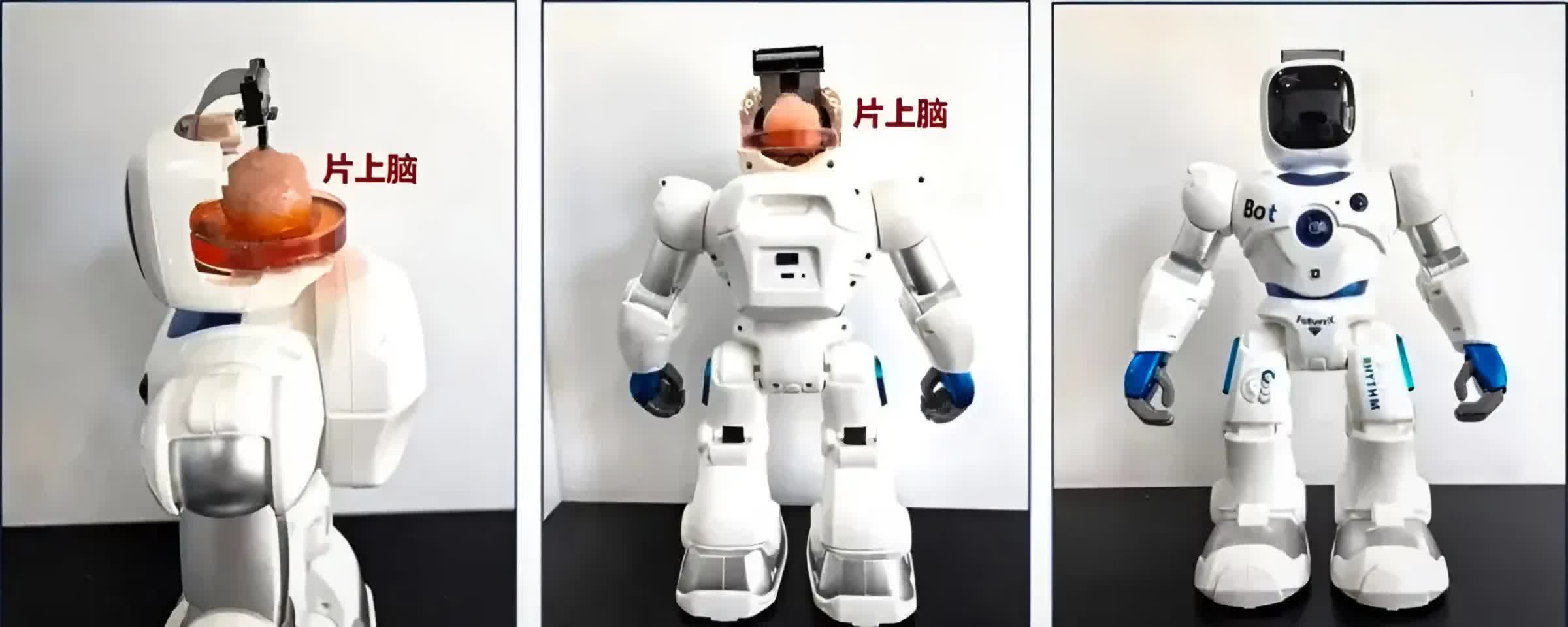

Past their speedy utility in robotics, researchers intention to make use of organoids for mind restore by means of transplantation, probably aiding stroke victims and others with mind accidents.
“The transplant of human mind organoids into dwelling brains is a novel methodology for advancing organoid improvement and performance,” the examine reads. “Organoid grafts have a host-derived purposeful vasculature system and exhibit superior maturation.”
Regardless of these promising developments, the analysis remains to be at an early stage, and vital questions stay concerning the feasibility of repairing broken mind tissues with organoids. Nonetheless, the potential is intriguing. Futurism notes that experiments on the College of Pennsylvania demonstrated that transplanting human neurons into rat brains with broken visible cortices might revive the affected areas and restore response to stimuli like gentle.
Of their current work, the Chinese language researchers used low-intensity ultrasound to reinforce the mixing of organoids into host brains. This system improved the formation of neural networks, suggesting a non-invasive methodology to assist sufferers with mind harm. Whereas this ultrasound therapy might facilitate the connection between organoids and computing interfaces, it represents a preliminary step in the direction of the long run objective of utilizing lab-grown mind tissue to revive human mind capabilities.
This analysis underscores the potential of mixing organoid expertise with BCIs, paving the best way for superior therapeutic methods and clever robotic techniques. It additionally confirms findings in related research, resembling Indiana College Bloomington’s “Brainoware” analysis.
Picture credit score: Maxuser
[ad_2]
Source link





/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25524175/DSCF8101.jpg)




















