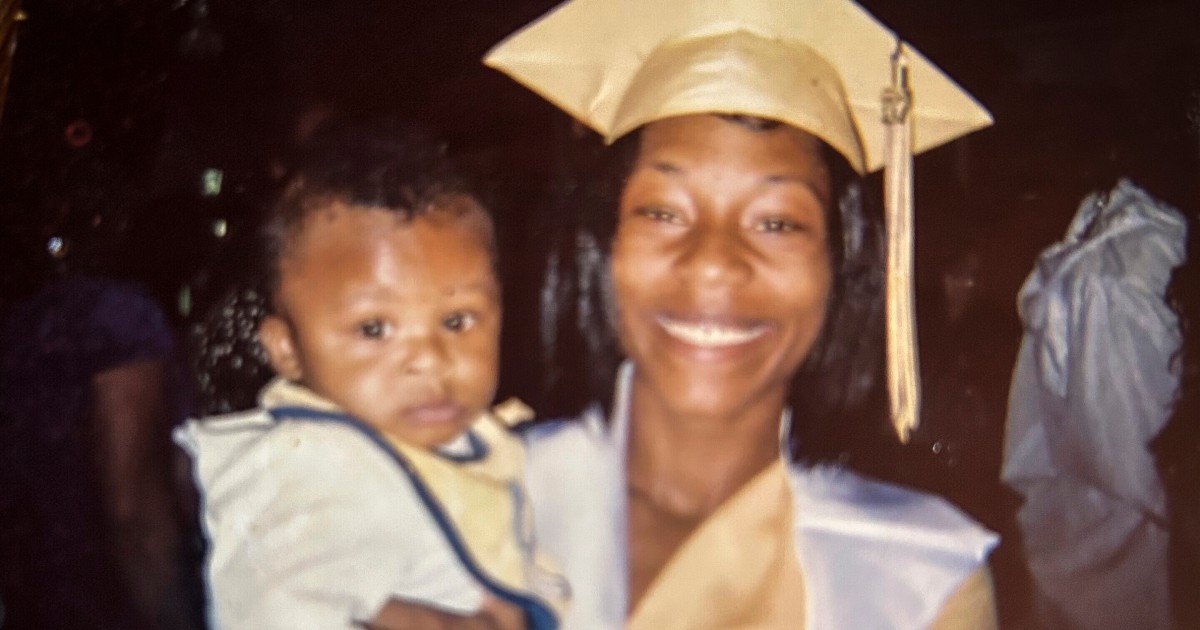[ad_1]

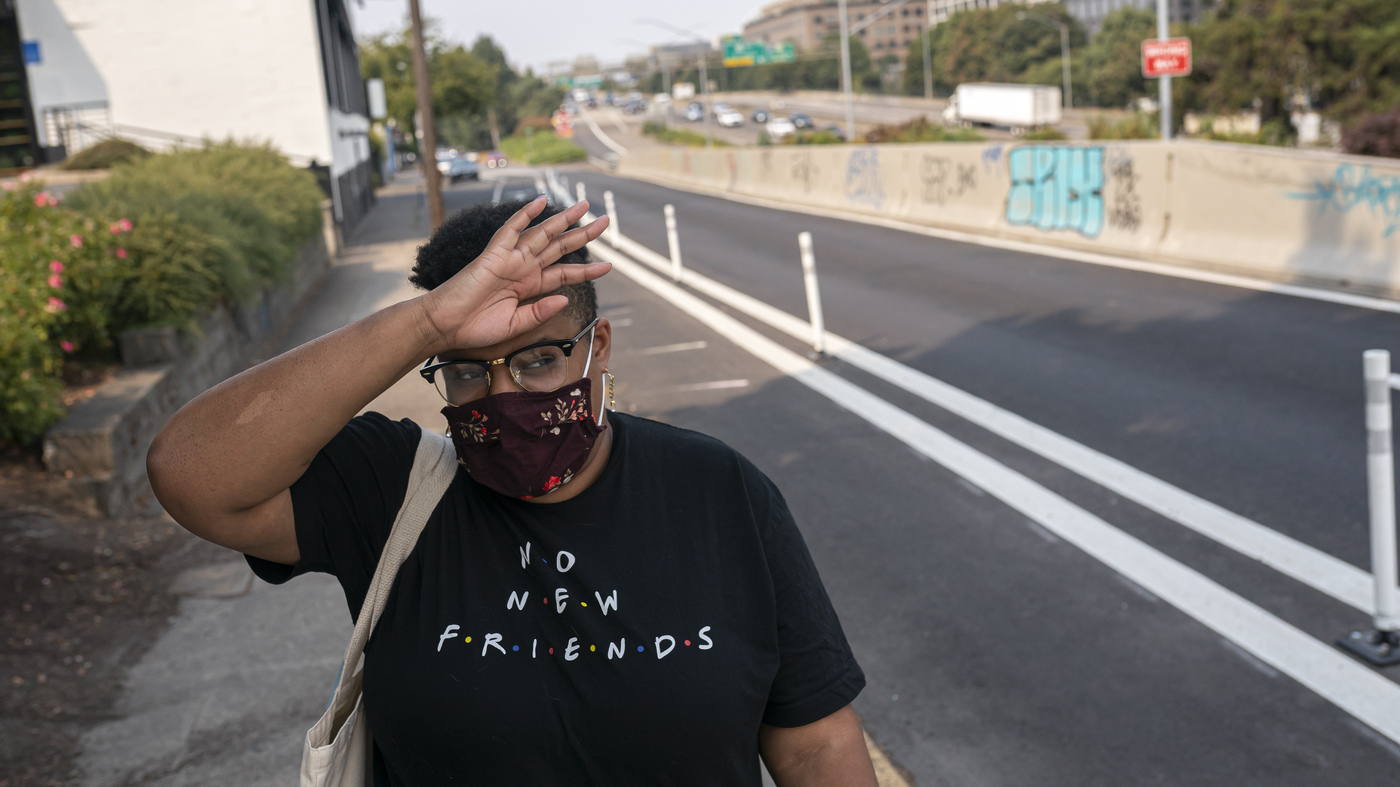
Katherine Morgan wipes sweat from her brow whereas strolling to work throughout a record-breaking warmth wave in Portland in 2021. Scientists say that warmth wave would have been nearly unattainable with out human prompted local weather change.
Nathan Howard/AP
disguise caption
toggle caption
Nathan Howard/AP
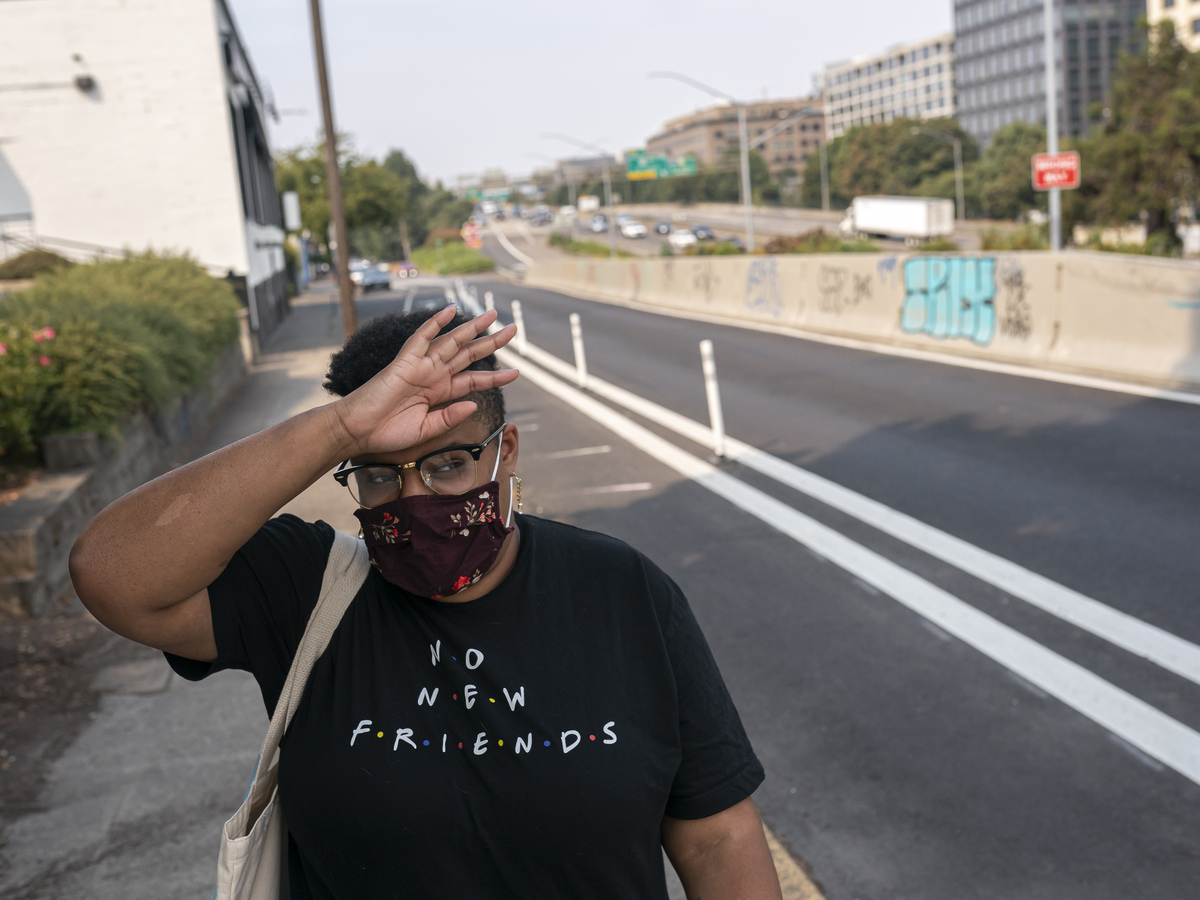

Katherine Morgan wipes sweat from her brow whereas strolling to work throughout a record-breaking warmth wave in Portland in 2021. Scientists say that warmth wave would have been nearly unattainable with out human prompted local weather change.
Nathan Howard/AP
Chances are high, in the event you reside on Earth, you’ve got skilled some unusual, or downright harmful, climate in the previous few years. Perhaps it was a warmth wave that was hotter and longer than you’d ever skilled. Or a thunderstorm that dropped a scary quantity of rain. Or a strong hurricane that appeared to materialize in a single day.
Local weather change is a part of that story. Excessive climate is extra possible because the Earth will get hotter. However such sweeping statements can really feel impersonal, when actually what you need to know is: has local weather change affected me?
“You might have some excessive climate catastrophe, and folks need to know: Did local weather change flood my home? Did local weather change make it so scorching that my energy went out?” says Michael Wehner, a senior scientist at Lawrence Berkeley Nationwide Laboratory who research how local weather change influences excessive climate. “These are good questions.”
Now, scientists can reply these questions with an increasing number of certainty. For some sorts of climate, it is change into attainable to say precisely how a lot worse it was due to local weather change. Or that with out world warming, the catastrophe wouldn’t have occurred in any respect.
Local weather change makes each warmth wave worse
Warmth waves have the clearest connection to world warming. “It appears apparent that as the worldwide local weather warms, warmth waves would additionally heat,” says Wehner.
However how a lot hotter, precisely?
Scientists have quantified that. “For backyard selection warmth waves – like the most well liked day of the yr, or the most well liked day each 10 years – within the U.S., local weather change has elevated that warmth wave’s temperature by 3 to five levels Fahrenheit,” Wehner explains.
You may see these further levels in motion when warmth data fall time and again. Hundreds of thousands of individuals residing in additional than a dozen cities within the Western U.S. and Texas skilled record-breaking temperatures throughout a warmth wave this June. Many cities, resembling Phoenix, Las Vegas and Houston, set new warmth data nearly each summer time.
However scientists can go even additional, utilizing supercomputers and superior statistics to research essentially the most excessive warmth waves, just like the one which killed tons of of individuals in Canada and the Pacific Northwest in 2021. Temperatures reached 120 levels in elements of Canada, and hit 115 levels in Oregon and Washington.
When scientists analyzed how local weather change affected that warmth wave, they discovered one thing startling. “It was nearly unattainable with out local weather change,” says Wehner.
One other option to say that? Local weather change prompted final summer time’s excessive warmth wave.
Most scientists talk with statistics. That has upsides and disadvantages
Local weather scientists are inclined to avoid the phrase “trigger.” They decide as a substitute for numbers that designate precisely how possible an excessive climate occasion was, in comparison with a world earlier than people began burning giant portions of fossil fuels.
However many scientists are conscious that, for the general public, these numbers may not imply a lot.
“Lets say [the 2021 Pacific Northwest heat wave] was a 1 in 1000 yr occasion in right this moment’s local weather. Or that it was about 150 occasions extra possible right this moment than it was in a preindustrial local weather, ” says Luke Harrington, a senior analysis fellow at Victoria College of Wellington in New Zealand who research local weather change and excessive climate. “However that is most likely not helpful [if you want] to grasp that [the heat wave] was principally not going to occur in a preindustrial world.”
Wehner factors out that, for extra frequent sorts of harmful climate, extra detailed numbers could be useful as a result of they inform individuals how typically they will want to deal with sure occasions.
For instance, think about there is a thunderstorm that drops much more rain than typical and floods your home. Prior to now, such a storm would have been very uncommon – a as soon as in a lifetime occasion.
Scientists would possibly examine that storm and discover it was 10 occasions extra prone to occur due to local weather change.
“If that occasion is 10 occasions extra possible, meaning it should occur as soon as each 7 years,” as a substitute of as soon as in a lifetime, explains Wehner. In different phrases, climate that after was very uncommon is now taking place usually. And understanding that may assist individuals plan for the long run.
Sooner or later, local weather change info could also be a part of common climate forecasts
The analysis strategies that make this attainable are very new, within the scheme of issues. Typically, science strikes slowly. However the science of discovering local weather fingerprints in particular person climate disasters has gone from infancy to maturity in lower than 20 years, partially due to the large demand for details about how world warming is altering our lives.
“There is a clear demand for this from the general public,” says Wehner. He says the analysis methods have superior to the purpose the place individuals with much less tutorial coaching might do the work. “Identical to climate forecasting, you can rent professionals to do that,” he explains.
The satellite tv for pc climate service for the European Union is piloting such a service, which might analyze how a lot local weather change contributed to particular person climate occasions in Europe.
That will unlock time for local weather scientists to give attention to essentially the most urgent questions that also stay about excessive climate and world warming.
Some sorts of climate are tougher for scientists to check
Some sorts of climate are so complicated that it’s nonetheless troublesome for scientists to pinpoint the affect of local weather change on particular person occasions, even when the general connection to local weather change is well-understood.
And at last, naturally this #heatwave too is strengthened by local weather change.
Rising frequency, period and depth of heatwaves with world warming is probably essentially the most established truth within the attribution science. pic.twitter.com/V27Hmn9Hog
— Mika Rantanen (@mikarantane) June 13, 2022
For instance, wildfires are getting extra widespread and intense because the Earth will get hotter. International warming dries out vegetation and soil and makes scorching and dry climate circumstances extra possible.
However scientists aren’t capable of say precisely how a lot worse, or extra possible, a selected wildfire was due to world warming.
That is partly as a result of people can play such an energetic position in the place fires begin and the way giant they get. Most wildfires are began by people – for instance, by a campfire, energy line or perhaps a rogue cigarette. Human land administration dictates how a lot vegetation resembling timber, shrubs or grass is out there to feed the fireplace. And firefighters affect how giant the fireplace will get and the place it burns.
“Any hearth has so many components happening, and solely a few of them are carefully associated to the local weather,” says Megan Kirchmeier-Younger, a analysis scientist at Atmosphere and Local weather Change Canada who research excessive climate.
Attributing particular person hurricanes to local weather change can be troublesome. Hurricanes are each complicated and comparatively uncommon in comparison with different sorts of excessive climate – particularly since solely a small fraction of the storms that type really make landfall.
That small knowledge set makes it troublesome to match the consequences of storms that occur right this moment, with world warming, to storms that occurred earlier than people prompted world warming.
Nonetheless, in lots of circumstances scientists are capable of quantify the impact of local weather change on hurricane rain. Researchers discovered that local weather change prompted as much as 15% extra rain to fall throughout Hurricane Harvey in 2017. One other examine seemed on the total 2020 hurricane season and located that local weather change elevated excessive rain by 10% for the season as an entire.
However researchers are nonetheless determining how local weather change causes different adjustments in hurricanes, says Jill Trepanier, who research local weather change and tropical cyclones at Louisiana State College.
For instance, hurricanes are getting extra highly effective, and storms usually tend to quickly intensify. Hotter ocean water is usually responsible for each phenomena, however scientists do not perceive what’s taking place properly sufficient to say {that a} particular storm was “x” quantity extra highly effective, or intensified “y” %, extra shortly due to local weather change.
“We won’t say ‘That is the rationale they quickly intensify.’ We have not solved that drawback,” she says. “That is one thing we’re nonetheless engaged on.”
[ad_2]
Source link