[ad_1]
Did UK inflation stabilise in Could?
After surging in April, UK inflation is predicted to stabilise over the following few months — albeit remaining at historic ranges — earlier than reaching new heights later this yr.
Economists polled by Reuters anticipate UK client value progress to have hit 9.1 per cent on an annual foundation in Could. That determine would signify little change from the 40-year excessive of 9 per cent reached in April, when a leap within the nation’s vitality price-cap invoice led to a pointy rise from 7 per cent within the earlier month.
“We predict fewer fireworks within the Could CPI launch,” stated Ellie Henderson, economist at Investec. She forecast the headline client value index price to stay at 9 per cent in Could, however expects a mixture of firmer meals prices, increased petrol costs and one other steep uptick within the vitality value cap in October to push inflation into double figures within the second half of the yr.
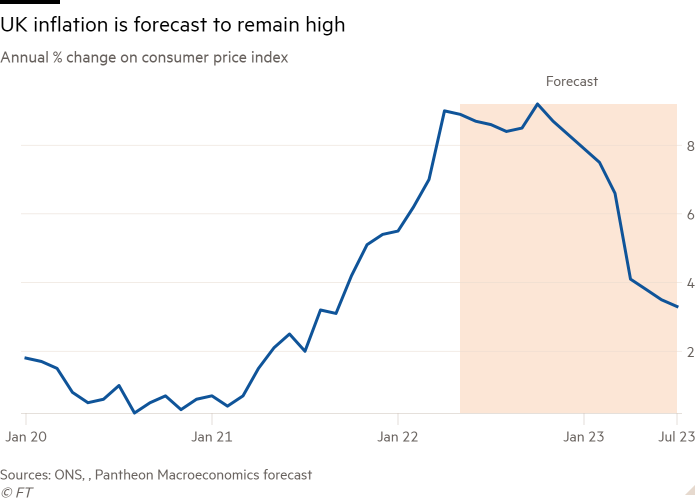
That is consistent with forecasts by the Financial institution of England which final week stated it expects inflation to common above 11 per cent within the final quarter however identified that “dangers to the inflation projection have been judged to be skewed to the upside.”
In an effort to carry inflation down nearer to the financial institution’s goal of two per cent, markets anticipate the financial institution to extend rates of interest to three per cent by the tip of the yr, from the present stage of 1.25 per cent. They’re additionally pricing a more-than 50 per cent likelihood of a 0.5 share level rate of interest rise on the BoE’s subsequent coverage assembly in August, which might be the sixth consecutive rise in charges. Valentina Romei
How far has eurozone inflation hit enterprise exercise in June?
Because the European Central Financial institution prepares to finish its period of simple cash and begin elevating rates of interest, economists can be monitoring whether or not enterprise exercise has grown at a slower tempo than anticipated within the face of surging inflation.
A month-to-month survey launched on Thursday is forecast to point out that eurozone enterprise exercise expanded in June, however at a slower tempo than in Could. Economists polled by Reuters predict that the ‘flash’ or early studying of the S&P World composite buying managers’ index for the eurozone will are available in at 54 in contrast with 54.8 a month earlier. Any quantity above 50 signifies progress somewhat than contraction.
That consensus estimate comes as companies and shoppers in Europe grapple with document inflation ranges stemming from provide chain disruption and the hovering value of products and vitality, exacerbated by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
Bert Colijn, a senior economist at ING, stated a central think about figuring out the well being of enterprise exercise can be how properly the providers trade — significantly in southern eurozone economies — has fared after the lifting of pandemic restrictions.
“Additionally necessary is whether or not the manufacturing sector continues to carry up regardless of provide chain issues and falling new orders,” he stated, including: “Vitality value progress stays problematic, however we additionally hear anecdotal proof of companies changing into extra cautious to cost by means of increased enter prices to the buyer.” Nikou Asgari
Norway could have been forward of different huge central banks in tightening financial coverage earlier than the present inflation scare. However even after three price rises since final September, Norges Financial institution nonetheless faces questions concerning the tempo of future will increase when it meets on Thursday.
Most economists anticipate it to boost rates of interest by 0.25 share factors to 1 per cent, and to point that it’s going to pace up future rises. Nordea, the Nordic area’s greatest financial institution, expects 4 extra will increase this yr after subsequent week, with the following one due in August, a extra speedy enhance than Norges Financial institution indicated in March. By the tip of 2023, its primary coverage price ought to be 3 per cent, Nordea believes.
Norway, western Europe’s main petroleum producer and one of many world’s richest nations, is affected by lots of the identical points as different developed nations — from rising inflation and wage stress to worries about future progress. However it additionally has the world’s largest sovereign wealth fund, which supplies a few quarter of the federal government’s price range, and sky-high revenues from oil and significantly fuel.
Might Norges Financial institution be tempted to observe the US Federal Reserve with a big price rise? The Nordea economists don’t imagine so, arguing that as 94 per cent of households have floating mortgage charges (versus about 10 per cent within the US) Norway’s coverage price is successfully transmitted to people, lessening the necessity for shock rises of 0.5 share factors or extra. Richard Milne
[ad_2]
Source link



























