[ad_1]
The Meals and Drug Administration could also be one step nearer towards what might be the primary approval of a drug that makes use of the groundbreaking gene-editing software CRISPR.
The drug, referred to as exa-cel, treats sickle cell illness, an inherited blood dysfunction that impacts an estimated 100,000 folks within the U.S., most of whom are Black, in response to the Facilities for Illness Management and Prevention.
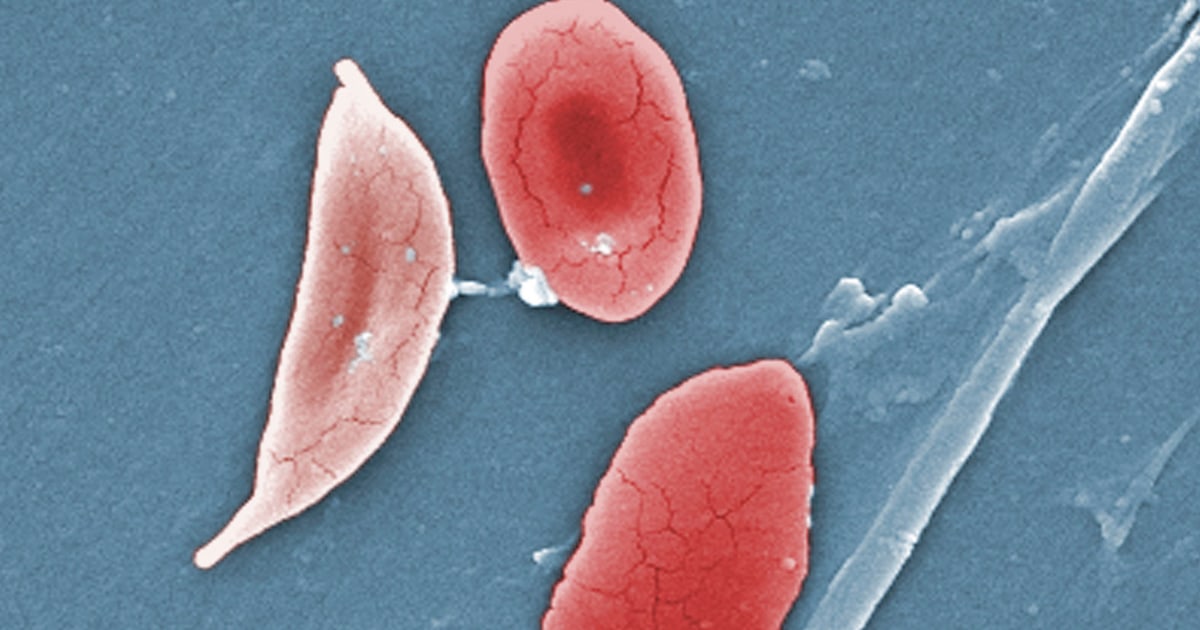
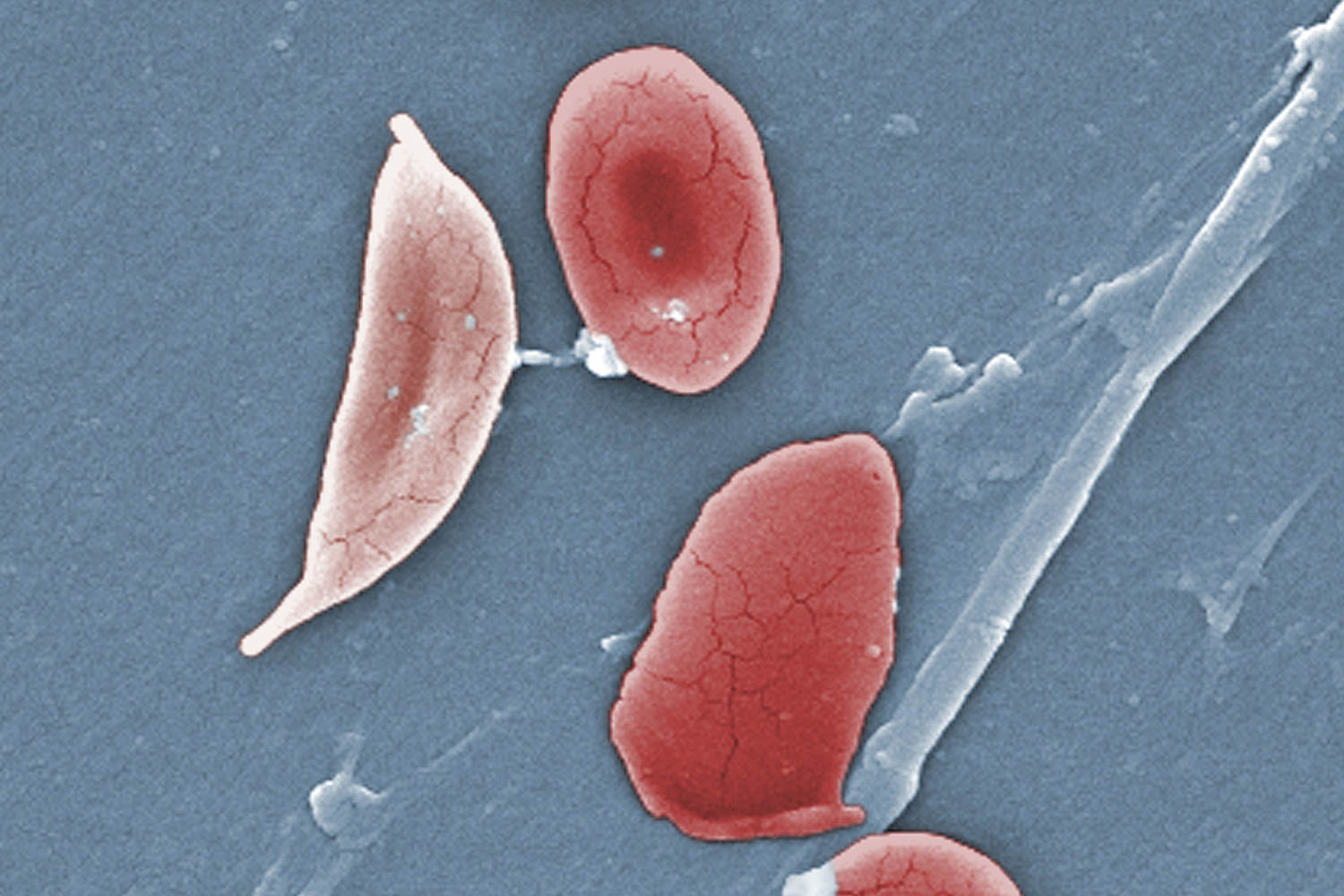
The sickness causes the physique’s crimson blood cells, often disk-shaped, to tackle a crescent or sickle form. When this happens, the cells can clump collectively, resulting in clots and blockages within the blood vessels. This will end in a spread of problems, together with excruciating ache, hassle respiratory or stroke.
“The promise of a universally obtainable, probably healing choice for people with sickle cell illness is revolutionary,” Dr. Biree Andemariam, hematologist and director of the New England Sickle Cell Institute on the College of Connecticut. Andemariam has consulted for Vertex Prescription drugs, which makes exa-cel.
The sickness is continual and the one identified treatment is a bone marrow transplant from a donor, which carries the danger of rejection.
The gene-editing drug, from Vertex together with CRISPR Therapeutics, would remove the necessity for a donor. As a substitute, it really works by altering the DNA within the affected person’s blood cells.
Exa-cel makes use of CRISPR, a gene-editing software that’s in a position to goal sure stretches of DNA and snip them out, primarily deleting the undesirable part that, within the case of sickle cell illness, causes the cells to tackle a crescent form.
On Tuesday, an FDA advisory committee reviewed the drug in an all-day assembly. These advisory conferences are often one of many ultimate steps earlier than the company decides whether or not to approve a drug. The FDA is predicted to difficulty a ultimate ruling by Dec. 8.
No drug that makes use of CRISPR gene-editing — which was invented in 2009 — has been granted FDA approval. What’s extra, Tuesday’s assembly regarded completely different than previous advisory committee conferences. On this case, the panel was not requested to judge the protection and effectiveness of Vertex’s drug, which is looking for approval for folks age 12 and up with extreme sickness.
As a substitute, the main focus was on the “off-target” results of CRISPR — that’s, when the know-how makes cuts to different stretches of the DNA aside from the meant goal — and the way the FDA ought to take into consideration these dangers shifting ahead.
It’s unclear what results an off-target edit would have on a affected person — it solely relies on the place it occurs within the DNA.
“Off-target enhancing doesn’t essentially imply that there’s going to be a nasty end result,” mentioned committee member Scot Wolfe, a professor of molecular, cell and most cancers biology at UMass Chan Medical College.
“There appears to be numerous uncertainty, numerous unknowns, about what these off-target adjustments would possibly imply,” mentioned committee member Lisa Lee, an epidemiologist and the director of scholarly integrity and analysis compliance at Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State College.
“Are these unknowns extra dangerous than not permitting this to go ahead?” Lee requested.
Vertex Prescription drugs offered analysis findings on 46 individuals who acquired the remedy. Among the many 30 sufferers with a minimal of 18 months of follow-up, 29 now not skilled extreme ache crises.
The corporate mentioned there was no proof of “off-target” results from the remedy, however committee members questioned whether or not Vertex’s evaluation was thorough sufficient.
“I’m not questioning that this product is essential for our sufferers,” mentioned committee member Dr. Joseph Wu, the director of the Stanford Cardiovascular Institute. “I’m simply saying we’re at a degree through which this factor goes to take off and wouldn’t or not it’s good to have extra extra information.”
A giant step ahead however not a easy treatment
Vertex has not disclosed the worth of gene remedy however, if accepted, it’s anticipated to be extraordinarily costly, probably costing as a lot as $2 million per affected person, in response to a report from the Institute for Scientific and Financial Evaluate, a nonprofit group that helps decide truthful costs for medication.
Dr. Stephan Grupp, chief of the remedy and transplant part of Kids’s Hospital of Philadelphia, who consults for Vertex, mentioned in an e-mail that if accepted, the step subsequent could be to verify sufferers can get entry.
“I do assume that they’re going to need to be numerous questions answered relating to entry,” Andemariam mentioned.
Whereas exa-cel is technically a one-time remedy, the method includes a lot of steps.
It begins by extracting stem cells from the affected person’s blood. These stem cells are edited with exa-cel within the lab to delete the snippet of DNA that causes the cells to warp. Earlier than these cells might be reinfused again into the affected person, nevertheless, the affected person should bear chemotherapy to kill off cells that produce the sickle-shaped cells.
Observe NBC HEALTH on Twitter & Fb.
[ad_2]
Source link