[ad_1]
Yves right here. This publish comprises a cautious and credible evaluation of how marked deviation from regular temperature ranges (right here within the sizzling path in Mexico) will increase default ranges, which then leads to constrained lending for a time period afterward. The influence is granular, on the municipal degree fairly than nation-wide. The authors supply some recommendations, primarily on the credit score/monetary entrance, however there may be not a lot you may to do ameliorate decrease crop yields and employee productiveness.
By Sandra Aguilar-Gomez, Assistant Professor of Economics Universidad De Los Andes. Initially printed at VoxEU
A current report from the Worldwide Panel on Local weather Change reveals a constant rise in excessive warmth days, affecting agriculture and past. Financial repercussions embrace decreased labour productiveness and elevated operational prices. Latest research additionally emphasise local weather’s monetary sector influence, particularly in low- and middle-income economies. This column delves into Mexican monetary vulnerabilities, revealing the hyperlink between excessive warmth and elevated delinquency charges, significantly amongst small and medium-sized enterprises. Coverage should tackle these dangers, coupling local weather resilience with enhanced credit score entry for susceptible corporations.
Local weather change is anticipated to extend the frequency and depth of utmost climate occasions. Heatwaves are a rising concern, every year breaking temperature information (IPCC 2021). Determine 1 shows analyses of the latest evaluation report of the Worldwide Panel on Local weather Change (IPCC AR6). Through the previous half a century, there was a constant enhance within the variety of days above the ninetieth percentile of the native distribution. In agriculture, it is not going to come as a shock that analysis has discovered that crop yields are negatively impacted by deviations from optimum situations for plant progress. Nonetheless, the financial impacts of a warming world prolong past the agricultural sector: excessive temperatures make work disagreeable and make some items and companies extra enticing than others. Excessive temperatures additionally make individuals extra aggressive and worse at making choices. Economists have discovered that these impacts translate into corporations’ income by means of decreased labour productiveness, elevated employee absenteeism, and shifts in native demand. Operational prices additionally rise if corporations spend sources to mitigate a few of these impacts (for instance, utilizing extra air-con and shorter shifts for exhausted employees). In a current Vox column, Ponticelli et al. (2023) talk about empirical findings of plant productiveness reducing with temperature within the US, main within the medium run to smaller crops closing, rising focus within the manufacturing sector.
Determine 1 Linear developments over 1960–2018 for 3 temperature excessive indices: Annual most day by day most temperature (panel a), annual minimal day by day minimal temperature (panel b), and annual variety of days when day by day most temperature exceeds its ninetieth percentile from a base interval of 1961–1990 (panel c)
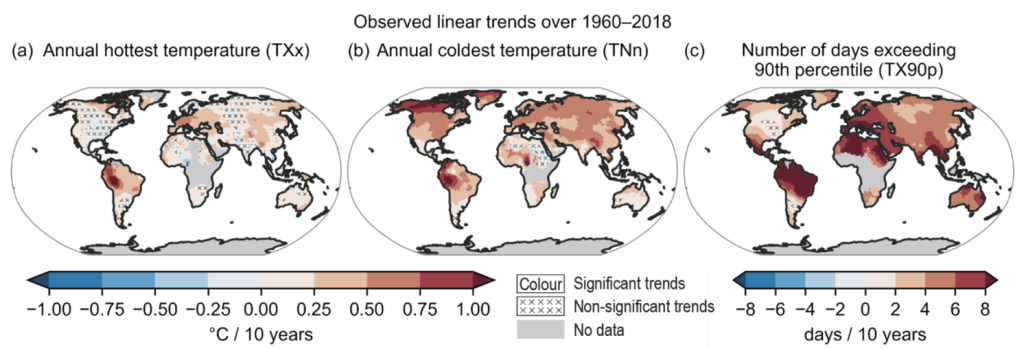
Supply: IPCC (2021) Determine 11.9.
Central banks and different monetary establishments are more and more involved in regards to the influence of those shocks on the monetary sector (Reinders et al. 2023). The impact of unfavourable climate on prices and demand might create liquidity shortages for corporations that would trigger solvency issues. In growing international locations, a number of situations recommend that corporations could also be extra susceptible. Suppose, as an example, the defaults generated by the shock enhance lenders’ uncertainty about debtors’ capability to repay their loans sooner or later. In that case, they may cost increased rates of interest for brand spanking new loans and cut back credit score availability, rising corporations’ credit score constraints. That is particularly related for credit score varieties for which the power to repay is extra unsure, akin to new small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) with scarce credit score historical past, or for corporations needing funding loans, which have longer maturity and better uncertainty about future income that the funding would generate. General, the influence of unbiased and identically distributed shocks could possibly be longer-lived when hitting credit score markets that deal much less effectively with informational asymmetries akin to these in low- and middle-income economies.
Furthermore, it is very important be aware that warming shouldn’t be projected to have an effect on international locations homogeneously. Most growing international locations are in areas with increased baseline temperatures. Therefore, even uniform warming might have disparate impacts resulting from onerous organic limits for agricultural yield and human well being. Nonetheless, present fashions venture vital heterogeneity in native warming, as proven in Determine 2. For all the explanations above, understanding the impacts of utmost climate occasions on the monetary sector in growing international locations is of excessive coverage relevance.
Determine 2 Projected modifications in annual most temperature (panels a to c) and annual minimal temperature (panels d to f) at 1.5°C, 2°C, and 4°C of world warming in comparison with the 1850–1900 baseline
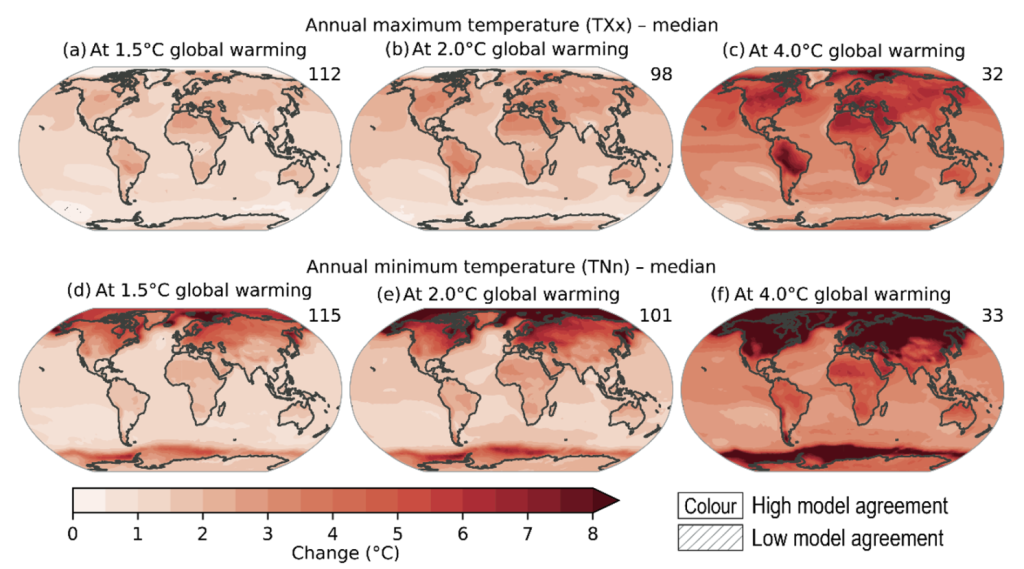
Supply: IPCC (2021) Determine 11.11.
In our current research (Aguilar-Gomez et al. 2024), my co-authors and I make use of a sturdy methodology and a complete dataset encompassing data on all loans prolonged by business banks to personal corporations in Mexico over a span of practically a decade. This permits us to delve into potential local weather vulnerabilities throughout the Mexican monetary system. Particularly, we estimate the influence of surprising days above the ninety fifth percentile of the temperature distribution on corporations’ monetary misery, with our main give attention to the delinquency charge, measured because the ratio of non-performing loans to complete excellent credit score in a county.
Our research reveals three primary findings:
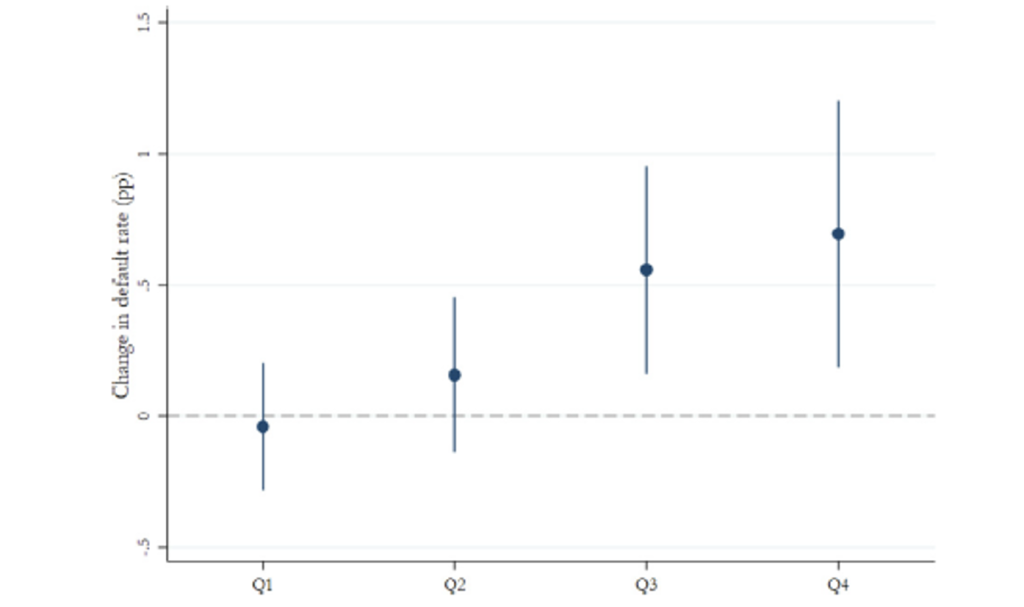
- Excessive warmth in a municipality raises its credit score delinquency charge, an impact pushed fully by small corporations defaulting on their loans. By way of magnitudes, ten uncommon days of utmost warmth throughout the earlier three months enhance the delinquency charge of SMEs by 0.17 share factors, equal to 4.4% of the noticed pattern imply (3.9%). Determine 3 shows this phenomenon by plotting the connection between the default charge and the times of utmost warmth within the earlier quarter. It additionally exhibits that the heatwave needs to be lengthy sufficient to trigger vital harm (i.e. 11 days). This discovering is in keeping with the notion that SMEs in growing international locations are much less geared up to deal with excessive temperatures, making it tougher to entry additional credit score in instances of economic stress. According to idea and former analysis (e.g. Schlenker and Roberts 2009, Blanc and Schlenker 2017), we discover that the unfavourable impact of utmost warmth is stronger in agriculture.
- Regional financial composition issues. Excessive warmth additionally has sizeable results on non-agricultural industries in areas with a sufficiently massive proportion of agricultural employees. Moreover, results within the non-agricultural sector are concentrated in companies and retail, that’s, non-tradable sectors that rely closely on native demand. The findings recommend that antagonistic situations in agriculture result in decreased native spending, inflicting spillover results into non-agricultural industries.
- By using numerous market integration measures in agriculture manufacturing, we discover that climate shocks have a stronger impact on credit score default amongst agricultural corporations in additional built-in markets. This result’s in keeping with the notion {that a} worth surge partially offsets a lower in native manufacturing attributable to excessive climate in additional remoted markets. Apparently, this proof implies that monetary establishments could also be much less susceptible to temperature shocks in comparatively remoted markets.
- One is perhaps much less involved about these outcomes if our information indicated that corporations recuperate and don’t carry longer-run implications of short-run shocks. We discover that temperature shocks cut back the variety of corporations with entry to credit score within the affected municipality for a while. Credit score composition additionally modifications after the climate shock: we discover a lower in credit score for investments and new corporations, together with an increase in rates of interest for brand spanking new loans. Particularly, publicity to excessive warmth interprets into elevated rates of interest for brand spanking new loans throughout the similar agency, heightened collateral necessities, and declined credit score entry. Collectively, the firm- and market-level outcomes present that in response to shocks, banks tighten credit score for 2 to 3 quarters, hindering entry to monetary flexibility when corporations most want it. These findings distinction with these present in superior economies, significantly the US, the place the proof means that corporations use credit score strains to handle liquidity throughout excessive climate (Brown et al. 2021, Collier et al. 2020). Mexican SMEs appear unable to make use of new loans equally.
Determine 3 Results of utmost temperatures on delinquency charges
Our findings present empirical help to the considerations relating to the potential results of utmost climate on the monetary system described, as an example, in Reinders et al. (2023). In response to accumulating proof, regulatory authorities, and central banks worldwide are calling for enhancements in measuring and monitoring local weather dangers, such that related actors can handle such dangers (Litterman et al. 2020). One coverage implication of our outcomes is that insurance policies looking for to cut back direct publicity to local weather shocks in banks’ steadiness sheets would ideally be carried out together with different complementary insurance policies, particularly in growing international locations. Such insurance policies might compensate for unintended penalties by deepening small and medium corporations’ entry to credit score, particularly when corporations are dealing with the influence of climate shocks.
[ad_2]
Source link

























