[ad_1]
Fb dad or mum Meta is seeing a “fast rise” in faux profile images generated by synthetic intelligence.
Publicly obtainable know-how like “generative adversarial networks” (GAN) permits anybody — together with menace actors — to create eerie deepfakes, producing scores of artificial faces in seconds.
These are “mainly images of people that don’t exist,” mentioned Ben Nimmo, World Menace Intelligence lead at Meta. “It isn’t really an individual within the image. It is a picture created by a pc.”
“Greater than two-thirds of all of the [coordinated inauthentic behavior] networks we disrupted this yr featured accounts that possible had GAN-generated profile footage, suggesting that menace actors might even see it as a approach to make their faux accounts look extra genuine and unique,” META revealed in public reporting, Thursday.
Investigators on the social media large “take a look at a mix of behavioral indicators” to establish the GAN-generated profile images, an development over reverse-image searches to establish greater than solely inventory picture profile images.
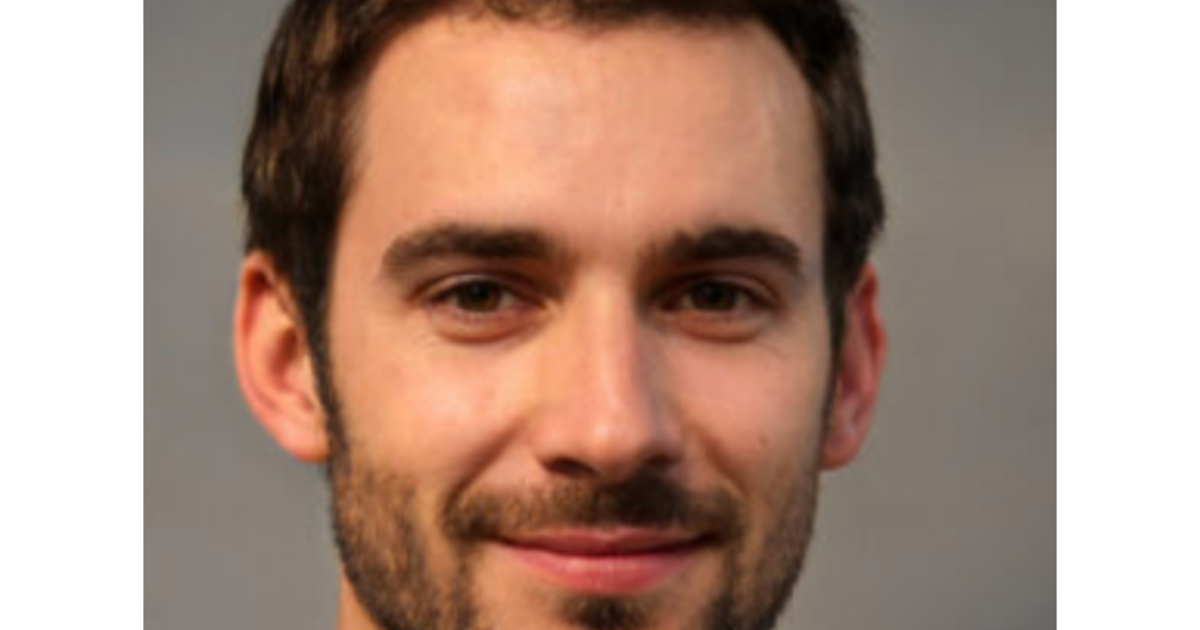
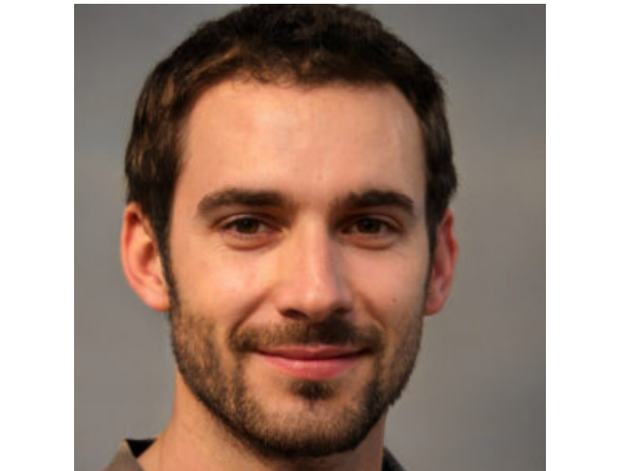
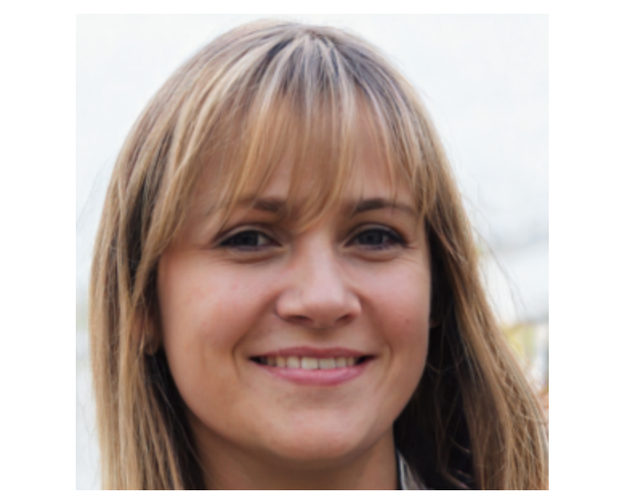
Meta has proven a number of the fakes in a current report. The next two photos are amongst a number of which might be faux. Once they’re superimposed over one another, as proven within the third picture, all the eyes align precisely, revealing their artificiality.
Meta
Meta
Meta/Graphika
These educated to identify errors in AI photos are fast to note not all AI photos seem picture-perfect: some have telltale melted backgrounds or mismatched earrings.
Meta
“There’s an entire group of open search researchers who simply love nerding out on discovering these [imperfections,]” Nimmo mentioned. “So what menace actors might imagine is an effective approach to conceal is definitely a great way to be noticed by the open supply group.”
However elevated sophistication of generative adversarial networks that can quickly depend on algorithms to provide content material indistinguishable from that produced by people has created an advanced recreation of whack-a-mole for the social media’s world menace intelligence staff.
Since public reporting started in 2017, greater than 100 nations have been the goal of what Meta refers to as “coordinated inauthentic conduct” (CIB).Meta mentioned the time period refers to “coordinated efforts to control public debate for a strategic objective the place faux accounts are central to the operation.”
Since Meta first started publishing menace studies simply 5 years in the past, the tech firm has disrupted greater than 200 world networks – spanning 68 nations and 42 languages – that it says violated coverage. Based on Thursday’s report, “america was essentially the most focused county by world [coordinated inauthentic behavior] operations we have disrupted through the years, adopted by Ukraine and the UK.”
Russia led the cost as essentially the most “prolific” supply of coordinated inauthentic conduct, based on Thursday’s report with 34 networks originating from the nation. Iran (29 networks) and Mexico (13 networks) additionally ranked excessive amongst geographic sources.
“Since 2017, we have disrupted networks run by folks linked to the Russian army and army intelligence, advertising corporations and entities related to a sanctioned Russian financier,” the report indicated. “Whereas most public reporting has centered on numerous Russian operations concentrating on America, our investigations discovered that extra operations from Russia focused Ukraine and Africa.”
“If you happen to take a look at the sweep of Russian operations, Ukraine has been persistently the one largest goal they’ve picked on,” mentioned Nimmo, even earlier than the Kremlin’s invasion. However america additionally ranks among the many culprits in violation of Meta’s insurance policies governing coordinated on-line affect operations.
Final month, in a uncommon attribution, Meta reported people “related to the US army” promoted a community of roughly three dozen Fb accounts and two dozen Instagram accounts centered on U.S. pursuits overseas, zeroing in on audiences in Afghanistan and Central Asia.
Nimmo mentioned final month’s removing marks the primary takedown related to the U.S. army relied on a “vary of technical indicators.”
“This specific community was working throughout a variety of platforms, and it was posting about normal occasions within the areas it was speaking about,” Nimmo continued. “For instance, describing Russia or China in these areas.” Nimmo added that Meta went “so far as we will go” in pinning down the operation’s connection to the U.S. army, which didn’t cite a selected service department or army command.
The report revealed that almost all — two-thirds —of coordinated inauthentic conduct eliminated by Meta “most continuously focused folks in their very own nation.” Prime amongst that group embrace authorities companies in Malaysia, Nicaragua, Thailand and Uganda who have been discovered to have focused their very own inhabitants on-line.
The tech behemoth mentioned it is working with different social media corporations to show cross-platform info warfare.
“We have continued to show operations operating on many various web providers directly, with even the smallest networks following the identical various strategy,” Thursday’s report famous. “We have seen these networks function throughout Twitter, Telegram, TikTok, Blogspot, YouTube, Odnoklassniki, VKontakte, Change[.]org, Avaaz, different petition websites and even LiveJournal.”
However critics say these sorts of collaborative takedowns are too little, too late. In a scathing rebuke, Sacha Haworth, government director of the Tech Oversight Venture known as the report “[not] definitely worth the paper they’re printed on.”
“By the point deepfakes or propaganda from malevolent international state actors reaches unsuspecting folks, it is already too late,” Haworth advised CBS Information. “Meta has confirmed that they don’t seem to be eager about altering their algorithms that amplify this harmful content material within the first place, and because of this we want lawmakers to step up and move legal guidelines that give them oversight over these platforms.”
Final month, a 128-page investigation by the Senate Homeland Safety Committee and obtained by CBS Information alleged that social media corporations, together with Meta, are prioritizing person engagement, progress, and income over content material moderation.
Meta reported to congressional investigators that it “take away[s] tens of millions of violating posts and accounts day-after-day,” and its synthetic intelligence content material moderation blocked 3 billion phony accounts within the first half of 2021 alone.
The corporate added that it invested greater than $13 billion in security and safety groups between 2016 and October 2021, with over 40,000 folks devoted to moderation or “greater than the dimensions of the FBI.” However because the committee famous, “that funding represented roughly 1 % of the corporate’s market worth on the time.”
Nimmo, who was immediately focused with disinformation when 13,000 Russian bots declared him lifeless in a 2017 hoax, says the group of on-line defenders has come a great distance, including that he not feels as if he’s “screaming into the wilderness.”
“These networks are getting caught earlier and earlier. And that is as a result of we’ve extra and extra eyes in increasingly locations. If you happen to look again to 2016, there actually wasn’t a defender group. The fellows taking part in offense have been the one ones on the sector. That is not the case.”
[ad_2]
Source link