[ad_1]
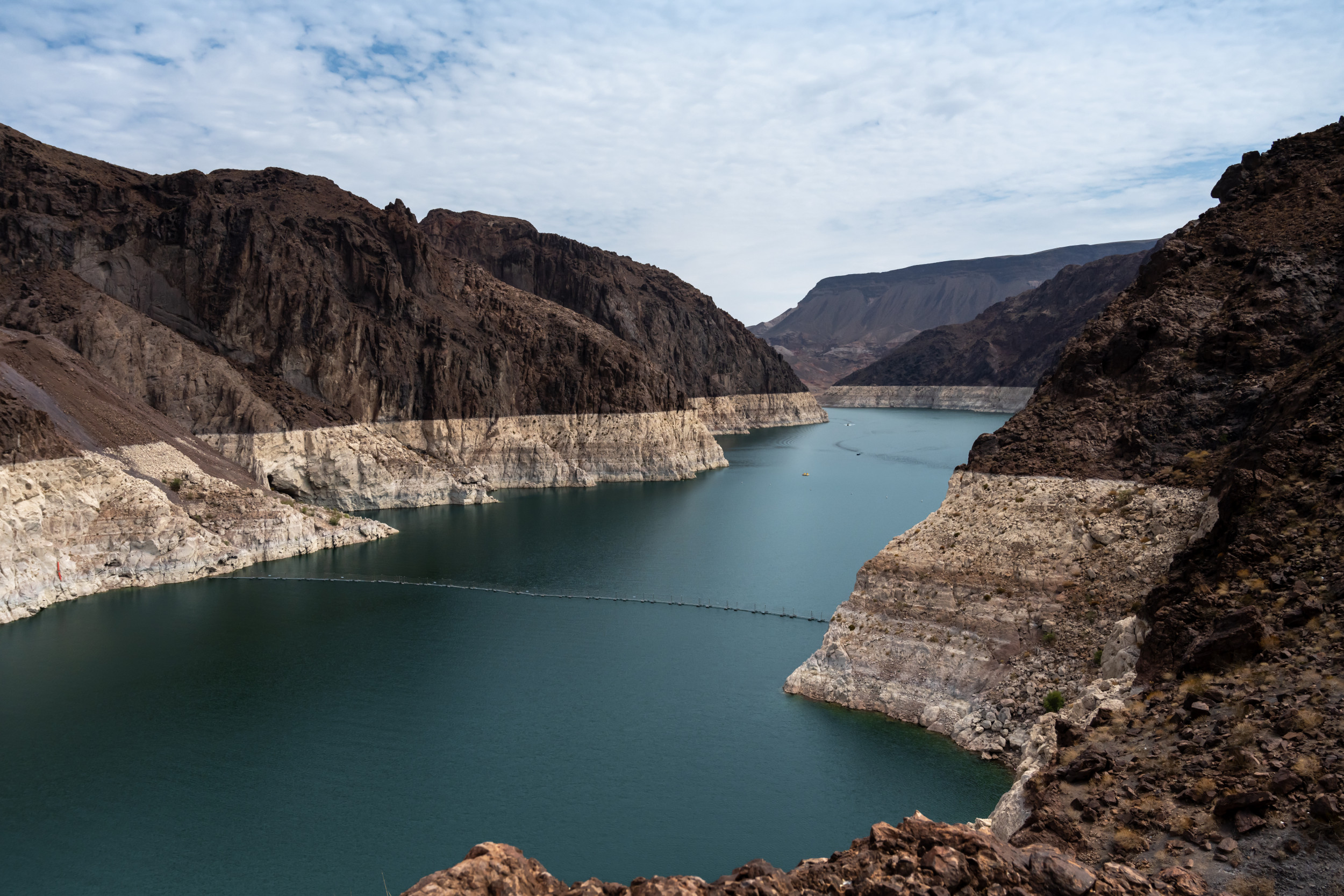
Lake Mead’s water ranges seem like trending down once more as summer time involves an in depth.
As of October 6, the reservoir’s water ranges stood at 1,065.71 ft. This can be a slight downturn from the center of September when ranges stood at 1066.46 ft.
Lake Mead borders Arizona and Nevada and is the most important man-made lake within the U.S. It’s an integral water supply and gives water for round 25 million folks dwelling within the Colorado River Basin. When the lake is full, it holds round 31 million acre-feet of water. However this has not been the case for a very long time.
There are severe considerations across the lake as its water ranges proceed to say no amid extreme drought circumstances within the area. As of now, the lake is barely round 30 p.c full.
“Water ranges in Lake Mead fluctuate seasonally,” Jennifer Pitt, Nationwide Audubon Society’s Colorado River Program Director instructed Newsweek. “It is most vital to regulate the change yr over yr for each Lakes Mead and Powell, which is indicative of whether or not the Colorado River water provide is growing, lowering, or secure. Each reservoirs are projected to have extra water in them on the finish of 2023 than they did on the finish of 2022, due to a really moist winter of 2022-2023.”
Originally of this yr, Lake Mead’s water ranges have been extremely low, at round 1044 ft. It fluctuated barely over the spring months till Might when ranges shot up.
The reservoir has seen current seasonal rains from Hurricane Hilary; nevertheless, most of this water replenishment comes from snowmelt within the higher Colorado basin, which has been above common this yr.
“Lake Mead ranges are up since March, which is an efficient factor,” Tom Corringham, a analysis economist on the Scripps Establishment of Oceanography at UC San Diego beforehand instructed Newsweek. “Many of the water within the Colorado River is from the higher basin. This has led to extra water being launched from Lake Powell which refills Lake Mead,” Corringham mentioned.
The above-average snowpack comes from a specific moist yr. Though the southwest has been in a drought for years, the area was battered with rain and snow storms all through the winter and early Spring.

J Gillispie/Getty
Whereas this has been a welcome supply of replenishment for the lake this yr, it’s unlikely to do a lot good in the long term.
For the water disaster to completely go away, the area would wish years of above-average rainfall.
Scientists consider local weather change is the primary offender for the extended drought. A change in climate patterns, paired with an overconsumption of water, has meant that Lake Mead’s assets are getting used extra rapidly than they’re being replenished.
“We will hope for extra snow in years to return, or we are able to scale back our consumption. Lowering water use is a proactive step we are able to take, and one we should always proceed to soak up the approaching years,” Corringham mentioned.
Do you’ve got a tip on a science story that Newsweek needs to be protecting? Do you’ve got a query concerning the results of local weather change? Tell us through science@newsweek.com.
[ad_2]
Source link