[ad_1]
Scientists who’ve monitored quite a few outbreaks of monkeypox in Africa say they’re baffled by the illness’s current unfold in Europe and North America.
Circumstances of the smallpox-related illness have beforehand been seen solely amongst folks with hyperlinks to central and West Africa. However up to now week, Britain, Spain, Portugal, Italy, U.S., Sweden and Canada all reported infections, largely in younger males who hadn’t beforehand traveled to Africa.
France, Germany, Belgium and Australia confirmed their first instances of monkeypox on Friday.
“I’m surprised by this. Every single day I get up and there are extra international locations contaminated,” stated Oyewale Tomori, a virologist who previously headed the Nigerian Academy of Science and who sits on a number of World Well being Group advisory boards.
“This isn’t the form of unfold we’ve seen in West Africa, so there could also be one thing new taking place within the West,” he stated.
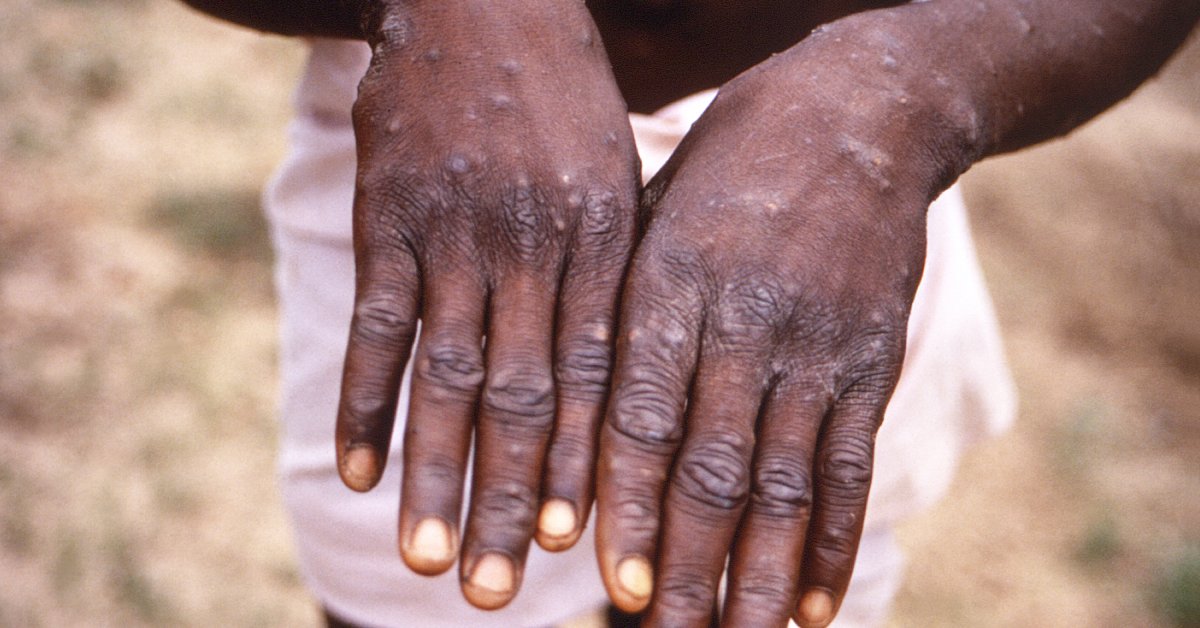
Monkeypox sometimes causes fever, chills, a rash and lesions on the face or genitals. WHO estimates the illness is deadly for as much as one in 10 folks, however smallpox vaccines are protecting and a few antiviral medication are additionally being developed.
One of many theories British well being officers are exploring is whether or not the illness is being sexually transmitted. Well being officers have requested docs and nurses to be on alert for potential instances, however stated the danger to the overall inhabitants is low.
Nigeria reviews about 3,000 monkeypox instances a 12 months, WHO stated. Outbreaks are often in rural areas, the place folks have shut contact with contaminated rats and squirrels, Tomori stated. He stated many instances are probably missed.
Tomori hoped the looks of monkeypox instances throughout Europe and different international locations would additional scientific understanding of the illness.
The WHO‘s lead on emergency response, Dr. Ibrahima Soce Fall, acknowledged this week that there have been nonetheless “so many unknowns when it comes to the dynamics of transmission, the scientific options (and) the epidemiology.”
On Friday, Britain’s Well being Safety Company reported 11 new monkeypox instances, saying that “a notable proportion” of the newest infections within the U.Ok. and Europe have been in younger males with no historical past of journey to Africa who had been homosexual, bisexual or had intercourse with males.
Authorities in Spain and Portugal additionally stated their instances had been in younger males who largely had intercourse with different males and stated these instances had been picked up when the lads turned up with lesions at sexual well being clinics.
Consultants have confused they have no idea if the illness is being unfold by intercourse or different shut contact associated to intercourse.
Nigeria hasn’t seen sexual transmission, Tomori stated, however he famous that viruses that hadn’t initially been identified to transmit by way of intercourse, like Ebola, had been later confirmed to take action after larger epidemics confirmed totally different patterns of unfold.
The identical could possibly be true of monkeypox, Tomori stated.
In Germany, Well being Minister Karl Lauterbach stated the federal government was assured the outbreak could possibly be contained. He stated the virus was being sequenced to see if there have been any genetic modifications that may have made it extra infectious.
Rolf Gustafson, an infectious illnesses professor, instructed Swedish broadcaster SVT that it was “very troublesome” to think about the scenario may worsen.
“We will definitely discover some additional instances in Sweden, however I don’t assume there will likely be an epidemic in any means,” Gustafson stated. “There may be nothing to counsel that at current.”
Scientists stated that whereas it’s doable the outbreak’s first affected person caught the illness whereas in Africa, what’s taking place now’s distinctive.
“We’ve by no means seen something like what’s taking place in Europe,” stated Christian Happi, director of the African Centre of Excellence for Genomics of Infectious Ailments. “We haven’t seen something to say that the transmission patterns of monkeypox have been altering in Africa. So if one thing totally different is going on in Europe, then Europe wants to analyze that.”
Happi additionally identified that the suspension of smallpox vaccination campaigns after the illness was eradicated in 1980 may inadvertently be serving to monkeypox unfold. Smallpox vaccines additionally shield towards monkeypox, however mass immunization was stopped many years in the past.
“Except for folks in west and Central Africa who might have some immunity to monkeypox from previous publicity, not having any smallpox vaccination means no person has any form of immunity to monkeypox,” Happi stated.
Shabir Mahdi, a professor of vaccinology on the College of Witwatersrand in Johannesburg, stated an in depth investigation of the outbreak in Europe, together with figuring out who the primary sufferers had been, was now important.
“We have to actually perceive how this primary began and why the virus is now gaining traction,” he stated. “In Africa, there have been very managed and rare outbreaks of monkeypox. If that’s now altering, we actually want to know why.”
___
Geir Moulson in Berlin, Jan M. Olsen in Copenhagen and AP reporters throughout Europe contributed to this report.
Extra Should-Learn Tales From TIME
[ad_2]
Source link



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Health-GettyImages-StrongGlutes-d834d403c3824ecc947fd2e1272beedc.jpg)






















