[ad_1]
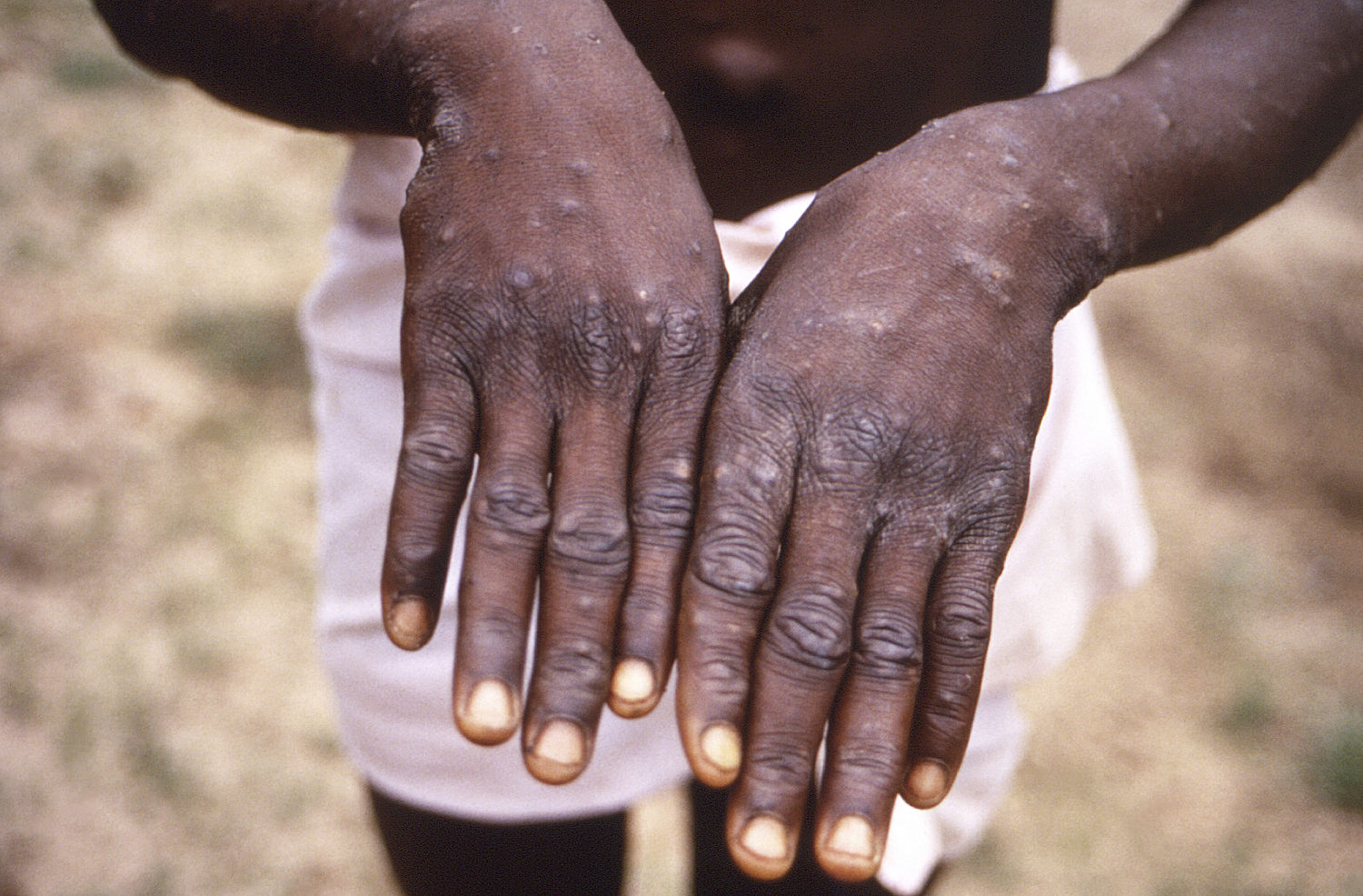
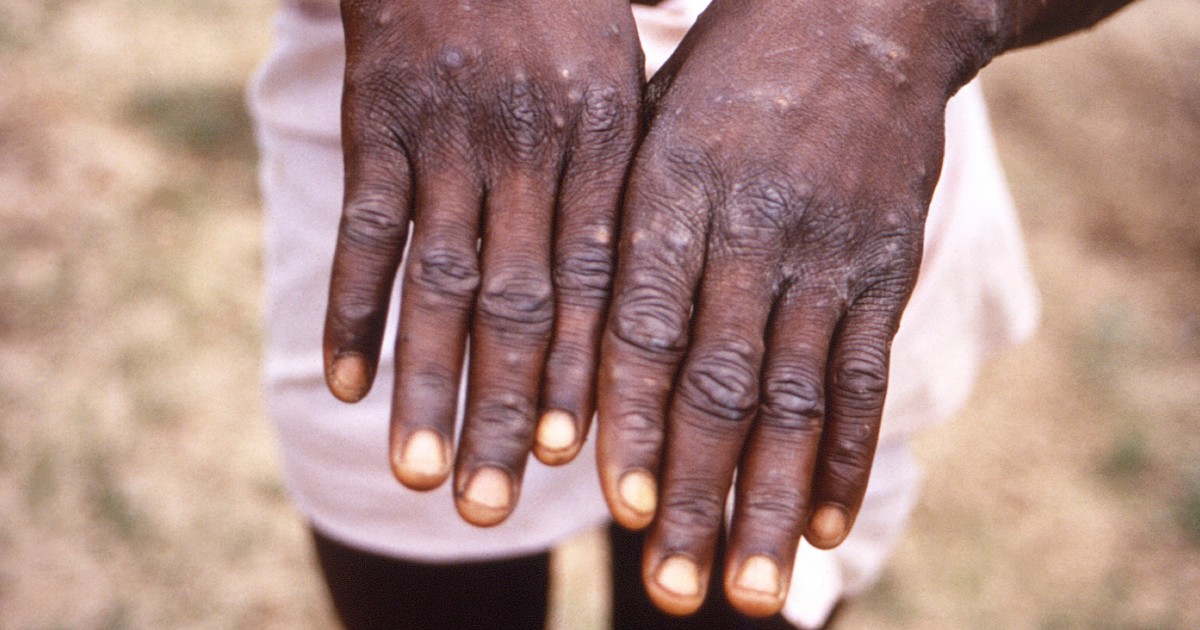
KINSHASA, Congo — As Congo copes with its largest outbreak of mpox, scientists warn discrimination in opposition to homosexual and bisexual males on the continent may make it worse.
In November, the World Well being Group reported that mpox, often known as monkeypox, was being unfold through intercourse in Congo for the primary time. That could be a vital departure from earlier flare-ups, the place the virus primarily sickened folks in touch with diseased animals.
Mpox has been in elements of central and west Africa for many years, however it was not till 2022 that it was documented to unfold through intercourse; a lot of the 91,00 folks contaminated in roughly 100 nations that yr had been homosexual or bisexual males.
In Africa, unwillingness to report signs may drive the outbreak underground, stated Dimie Ogoina, an infectious ailments specialist on the Niger Delta College in Nigeria.
WHO officers stated they recognized the primary sexually transmitted circumstances of the extra extreme kind of mpox in Congo final spring, shortly after a resident of Belgium who “recognized himself as a person who has sexual relations with different males” arrived in Kinshasa, the Congolese capital. The U.N. well being company stated 5 different individuals who had sexual contact with the person later turned contaminated with mpox.
“We’ve been underestimating the potential of sexual transmission of mpox in Africa for years,” stated Ogoina, who along with his colleagues, first reported in 2019 that mpox may be spreading through intercourse.
Gaps in monitoring make it a problem to estimate what number of mpox circumstances are linked to intercourse, he stated. Nonetheless, most circumstances of mpox in Nigeria contain folks with no identified contact with animals, he famous.
In Congo, there have been about 13,350 suspected circumstances of mpox, together with 607 deaths by the tip of November with solely about 10% of circumstances confirmed by laboratories. However what number of infections had been unfold by intercourse isn’t clear. WHO stated about 70% of circumstances are in kids beneath 15.
Throughout a current journey to Congo to evaluate the outbreak, WHO officers discovered there was “no consciousness” amongst well being staff that mpox might be unfold sexually, leading to missed circumstances.
WHO stated well being authorities had confirmed sexual transmission of mpox “between male companions and concurrently by heterosexual transmission” in numerous elements of the nation.
Mpox usually causes signs together with a fever, pores and skin rash, lesions and muscle soreness for as much as one month. It’s unfold through shut contact and most of the people get better with no need medical remedy.
Throughout the 2022 main worldwide outbreak, mass vaccination packages had been undertaken in some nations, together with Canada, Britain and the U.S., and focused these at highest threat — homosexual and bisexual males. However consultants say that’s not prone to work in Africa for a number of causes, together with the stigma in opposition to homosexual communities.
“I don’t suppose we’ll see the identical clamoring for vaccines in Africa that we noticed within the West final yr,” stated Dr. Boghuma Titanji, an assistant professor of medication in infectious ailments at Emory College Faculty of Medication in Atlanta.
She stated that the homosexual and bisexual males most susceptible to mpox may be afraid of coming ahead in a broad immunization program. International locations ought to work on methods to offer the photographs —if out there — in a approach that wouldn’t stigmatize them, she stated.
Dr. Jean-Jacques Muyemba, common director of Congo’s Nationwide Institute of Biomedical Analysis, stated two provinces in Congo had reported clusters of mpox unfold by intercourse, a regarding improvement.
There’s no licensed vaccine in Congo, and it will be exhausting to get sufficient photographs for any large-scale program, Muyemba stated. The nation is making an attempt to get a Japanese mpox vaccine, however regulatory points are complicating the state of affairs, he stated.
Globally, just one vaccine has been licensed in opposition to mpox, made by Denmark’s Bavarian Nordic. Provides are very restricted and even when they had been out there, they must be accredited by the African nations utilizing them or by WHO. Up to now, the vaccine has solely been out there in Congo by analysis.
Oyewale Tomori, a Nigerian virus professional who sits on a number of WHO advisory boards, stated African governments in all probability have too many competing priorities to ask the U.N. well being company or donors for assist securing vaccines.
“In Africa, mpox is almost certainly thought-about a low-priority nuisance,” Tomori stated.
He stated stronger monitoring, laboratory networks and higher availability of diagnostic provides could be extra useful to the continent than vaccines.
With out better efforts to cease the outbreaks in Africa, Ogoina predicted that mpox would proceed to contaminate new populations, warning that the illness may additionally spark outbreaks in different nations, just like the worldwide emergency WHO declared final yr.
“When the HIV pandemic began, it was amongst homosexual and bisexual males within the international north, and Africa thought it was not our downside,” he stated. “Earlier than we knew it, it got here to Africa, however we nonetheless thought heterosexual populations could be protected.”
Ladies of reproductive age now account for greater than 60% of recent HIV infections in Africa.
“I fear the identical factor will now occur with mpox,” he stated. “Until we deal with these outbreaks in Africa, this virus will hold coming again.”
[ad_2]
Source link